What is hyperhidrosis?
The term hyperhidrosis refers to excessive sweating that goes beyond the body’s need for thermal regulation. People with hyperhidrosis sweat excessively, regardless of physical exertion or ambient temperature.
This dysfunction can lead to significant mental, social, and occupational limitations and can thus cause a marked reduction in the quality of life.
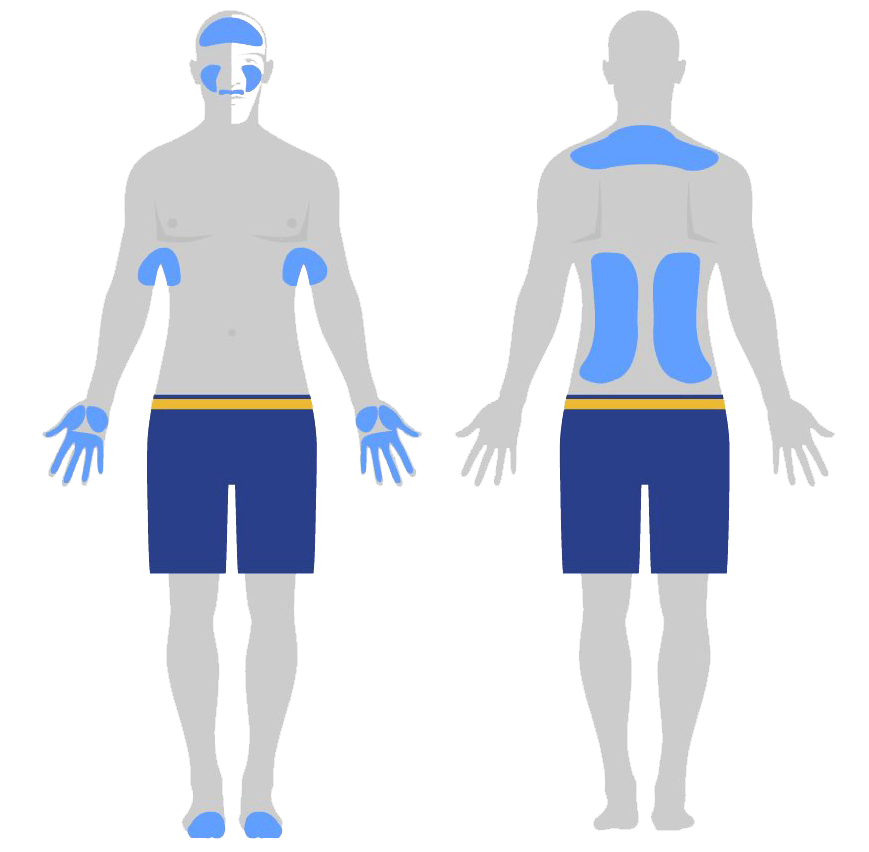
Hyperhidrosis can occur in different parts of the body. Hyperhidrosis often occurs on the hands (hyperhidrosis palmaris), on the face (hyperhidrosis facialis), on the soles of the feet (hyperhidrosis plantaris), and in the armpits (hyperhidrosis axillaris).
There are two types of hyperhidrosis
Local primary hyperhidrosis:
Focal hyperhidrosis, also called primary hyperhidrosis, is the most common form of hyperhidrosis and affects only individual areas of the body, especially the armpits, feet, hands, or face. About 2-3% of the population suffer from focal hyperhidrosis. This disease is wrongly considered by many to be untreatable.
As a rule, both halves of the body are equally affected by excessive sweating. Focal hyperhidrosis occurs independently of other disorders and begins as early as childhood or adolescence. Excessive sweating may begin immediately after waking up. During sleep, however, the affected person usually does not sweat, unless the ambient temperature is generally too high. Stress, anxiety, or pain can increase the effects of hyperhidrosis.
Secondary hyperhidrosis:
Secondary hyperhidrosis occurs as a result of an existing, underlying condition or as a side effect of taking medication or dietary supplements. Possible diseases that can cause excessive sweating are diabetes, cancer, obesity, gout, hyperthyroidism, and hormonal imbalances (e.g. during menopause). This form of hyperhidrosis usually affects the entire body. In contrast to primary hyperhidrosis, excessive sweating can also occur during sleep.